Using AWS Secrets Manager for Git Repository Access
Overview
This guide explains how to use AWS Secrets Manager to manage and retrieve credentials for accessing a Git repository within the Torque platform. By using Secrets Manager, you can securely store and retrieve access tokens, which are then utilized by Torque's asset discovery (agent) and provisioning (runner) components, simplifying repository credential management while adhering to organizational security policies.
Scope
This guide supports the use of third-party secret management services, specifically AWS Secrets Manager, to retrieve repository tokens for use in the Torque platform. This provides a flexible and secure way to manage repository credentials during asset discovery and provisioning processes.
Motivation
Integrating AWS Secrets Manager into Torque allows users to manage repository credentials in a more secure manner, facilitating seamless integration with Torque's asset discovery and provisioning capabilities. It enhances adaptability to customer policies on secrets storage and management, thus streamlining secure repository access within Torque.
Steps to Configure AWS Secrets Manager for Repository Access
Step 1: Configure the Secret in AWS Secrets Manager
- Log in to your AWS Account: Navigate to the AWS Management Console and go to Secrets Manager.
- Create a New Secret: Click on Store a new secret and select the option to store an access token or any necessary repository credentials.
- Configure Secret Details: Provide a name for your secret, such as
git-repo-token. Ensure that the secret name is descriptive and aligns with your organization's naming conventions.
Step 2: Create IAM Role with Required Permissions
- Create IAM Role: In your AWS account, create an IAM role with the required permissions to access the secret stored in AWS Secrets Manager.
- Permission Policy: Attach the following permission policy to the IAM role to allow access to retrieve secrets:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "SecretAccessPermission",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "secretsmanager:GetSecretValue",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
- Permission Policy: Attach the following permission policy to the IAM role to allow access to retrieve secrets:
- Add Trust Relationship: Add a trust relationship policy to allow the Torque cluster to assume this role.
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::046086677675:role/agent-sa-role"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
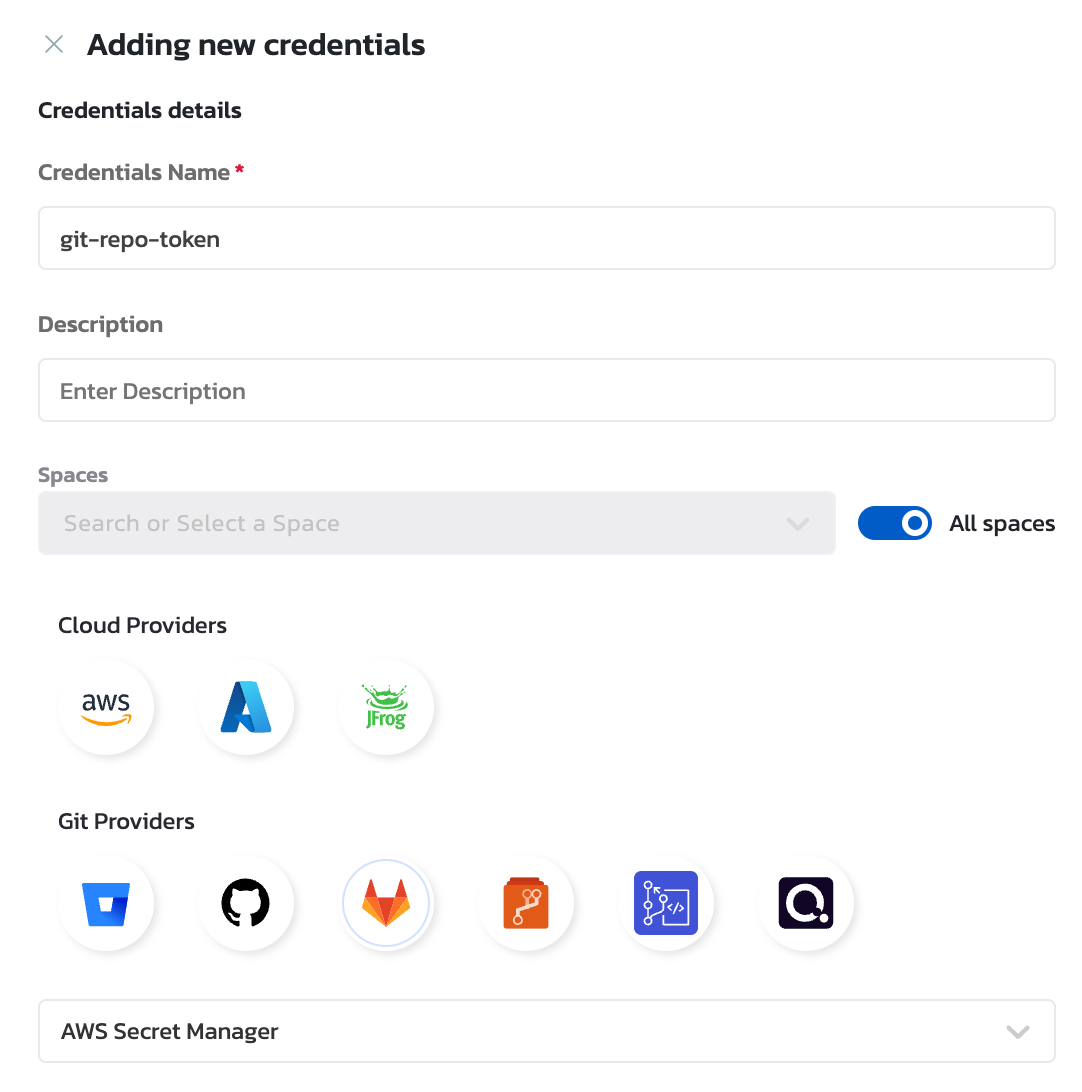
Step 3: Configure Git Credentials in Torque
- Install the Agent: Ensure that the Torque agent is installed.
- Navigate to Torque Credentials: In the Torque portal, navigate to the Account Admin -> Credentials page.
- Add New Git Credential: Click on Add New Credential and select the credential type as Gitlab. In the dropdown list, choose the Secret Manager option.
-
Fill Out Credential Details:
- Provide the Role ARN and External ID of the role created in Step 2.
- The following fields are mandatory:
- Role ARN: The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the IAM role created in Step 2.
- Secret ID: The identifier for the secret in AWS Secrets Manager, which can be either the secret name or the secret ARN.
- Secret Path: Represents the hierarchy of fields inside the secret's value.
- External ID is optional but can be provided if required by your security policies.
The secret will be used by Torque's asset discovery (agent) or provisioning (runner) components to interact securely with the Git repository.
Troubleshooting
-
Verify Secret Retrieval: You can manually verify that the secret can be retrieved using the AWS CLI or SDK to ensure proper configuration.
- Using AWS CLI:
aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id git-repo-token - Using AWS SDK (Python Example):
import boto3
client = boto3.client('secretsmanager')
response = client.get_secret_value(SecretId='git-repo-token')
secret = response['SecretString']
- Using AWS CLI:
-
Git Clone Validation: Ensure that the retrieved token is being used correctly to access the Git repository. You can test this by running the following command:
GIT_TOKEN=$(aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id git-repo-token --query SecretString --output text)
git clone https://$GIT_TOKEN@github.com/your-org/your-repository.git
Best Practices
- Regular Rotation: Regularly rotate the secrets in AWS Secrets Manager to minimize security risks.
- Access Control: Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to restrict access to the secret, ensuring only authorized users or services can retrieve it.
- Audit and Monitoring: Enable AWS CloudTrail to monitor access to your secrets and ensure compliance with your organization’s security policies.
Summary
By utilizing AWS Secrets Manager, you can securely store and manage Git repository credentials for use within the Torque platform, improving the security and compliance of your asset discovery and provisioning workflows. Follow the above steps to integrate Secrets Manager seamlessly with your Git operations in Torque.