Application Orchestration
Gaining agility and velocity in development and testing teams, usually requires adopting concepts like shift-left testing, where production-like environments are required to be in the disposed of all steps in the software development lifecycle. Production-like environment usually compose multiple automation process together to include both infrastructure, application and testing tools all together and enable them to the environment consumers.
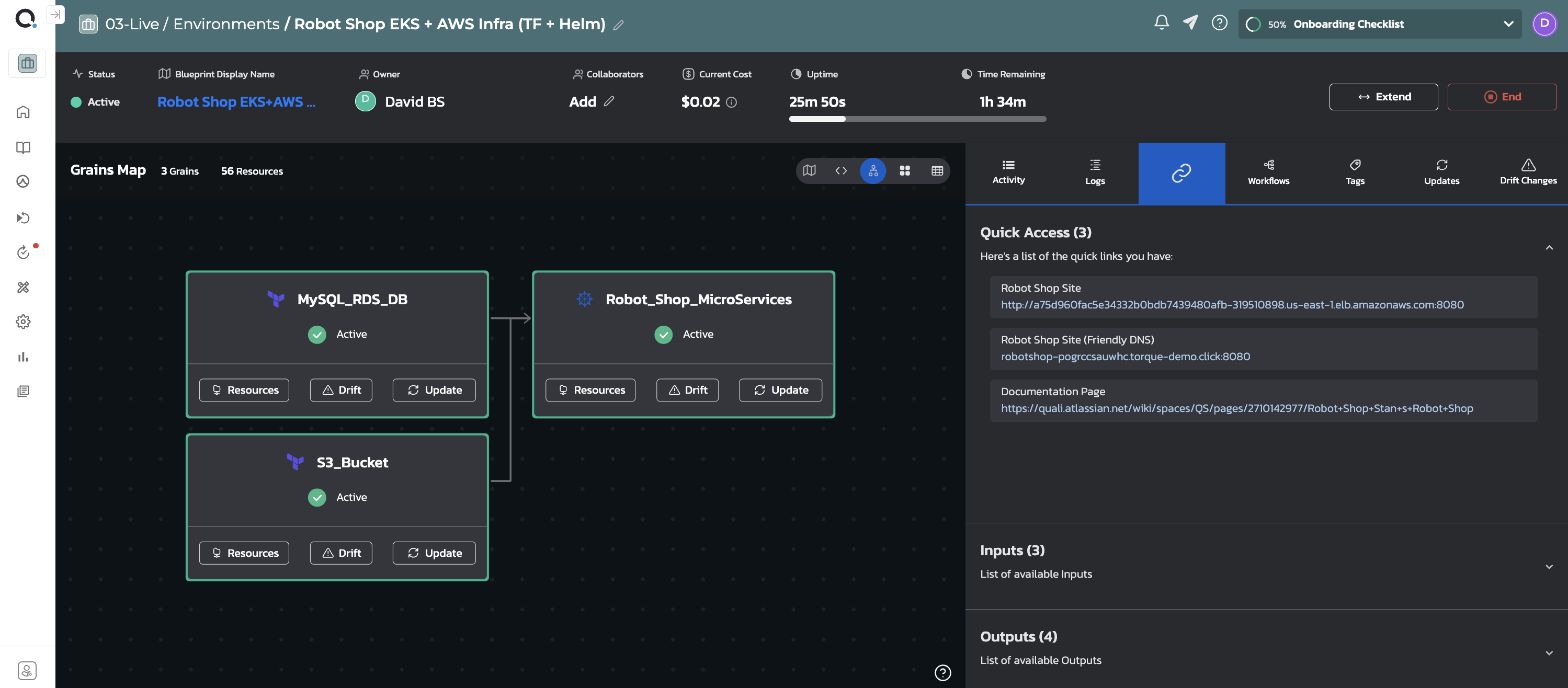
In the following example, a cloud native application, based on microservices requires dedicated AWS PaaS services to be launched to mimic a production deployment. The PaaS services are managed and orchestrated by the IT team, who adopted Terraform, while the application itself is orchestrated using Helm - the preferred Kubernetes orchestration tool by the DevOps team.
grains:
MySQL_RDS_DB:
kind: terraform
spec:
...
outputs:
- hostname
- connection_string
S3_Bucket:
kind: terraform
...
Robot_Shop_MicroServices:
kind: helm
depends-on: MySQL_RDS_DB, S3_Bucket
inputs:
- connectionString: '{{ .grains.MySQL_RDS_DB.outputs.connection_string }}'
...
In the example above, Torque normalized the various automation frameworks so they all share the same interface and can be used as "building-blocks" and pass information between them. Note how the connection string that was generated for the RDS database is passed into the microservice application so software components will be able to use the database.